We frequently come around circumstances where we want to store a gathering of information whether of comparable information types or non-comparable information types. We have seen Clusters in C++ which are utilized to store set of information of comparative information types at bordering memory areas.
Dissimilar to Exhibits, Designs in C++ are client characterized information types which are utilized to store gathering of things of non-comparable information types.
What is a construction?
A design is a client characterized information type in C/C++. A construction makes an information type that can be utilized to bunch things of potentially various sorts into a solitary kind.
Structures in C++:
A structure is a user-defined data type in C/C++. A structure creates a data type that can be used to group items of possibly different types into a single type.
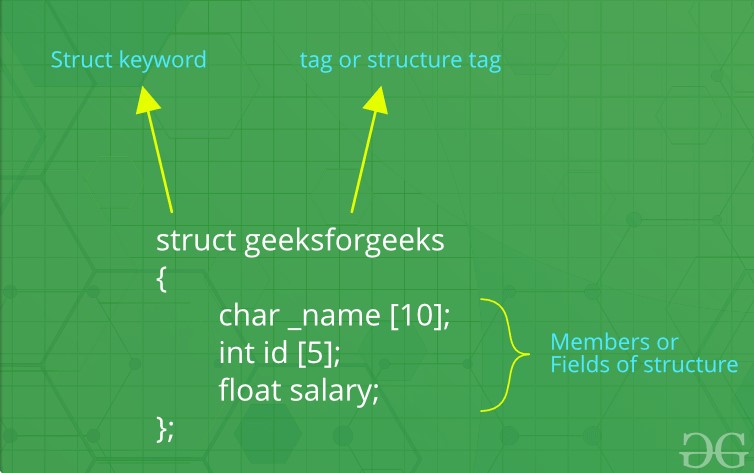
How to make a design?
The 'struct' watchword is utilized to make a construction. The overall punctuation to make a design is as displayed beneath:
struct structureName{ member1;
member2;
member3;
.
.
.
memberN; Structures in C++ can contain two sorts of individuals:
Information Part: These individuals are typical C++ factors. We can make a design with factors of various information types in C++.
Part Works: These individuals are ordinary C++ capabilities. Alongside factors, we can likewise incorporate capabilities inside a design statement.
Example:
- C++
In the above structure, the data members are three integer variables to store roll number, age and marks of any student and the member function is printDetails() which is printing all of the above details of any student.
How to pronounce structure factors?
A construction variable can either be proclaimed with structure statement or as a different statement like fundamental sorts.
C++
Note: In C++, the struct watchword is discretionary before in statement of a variable. In C, it is obligatory.
How to instate structure individuals?
Structure individuals can't be instated with statement. For instance the accompanying C program flops in accumulation.
Be that as it may, is considered right in C++ 11 or more.
- C++
The justification behind above blunder is straightforward, when a datatype is pronounced, no memory is designated for it. Memory is designated just when factors are made.
Structure individuals can be introduced with statement in C++. For Instance the accompanying C++ program Executes Effectively without tossing any Mistake.
x=0, y=1
x=0, y=20Structure members can be initialized using curly braces ‘{}’. For example, following is a valid initialization.
- C++
How to access structure elements?
Structure members are accessed using dot (.) operator.
- C++
x = 20, y = 1What is an array of structures?
Like other primitive data types, we can create an array of structures.
- C++
10 20
What is a structure pointer?
Like primitive types, we can have pointer to a structure. If we have a pointer to structure, members are accessed using arrow ( -> ) operator instead of the dot (.) operator.
- C++
1 2What is structure part arrangement?
In C++, a construction is equivalent to a class with the exception of a couple of contrasts. The most significant of them is security. A Construction isn't secure and can't conceal its execution subtleties from the end client while a class is secure and can conceal its customizing and planning subtleties. Find out about the distinctions among Designs and Class in C++.




.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment